Emissions Compliance
LNG offers immediate regulatory compliance as the most environmentally-friendly, readily available, fuel for deep-sea shipping today and in the foreseeable future.
LNG, in its fossil form, is compliant with both local emissions and greenhouse gas emissions regulations.
The use of LNG as a marine fuel enables ship owners and operators to comply with the IMO’s global sulphur cap and also current and proposed IMO-designated Emission Control Areas (ECAs), which restrict SOx, NOx and particulate matter emissions.
LNG far outperforms conventional marine fuels on a local emissions basis, which is particularly important in regard to human health issues in ports and coastal areas.
It emits virtually no sulphur oxides (SOx) and particulate matter (PM). Compared to existing heavy marine fuel oils, LNG can, depending on the technology used, emit up to 95% fewer nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. As such, it is compliant with both SOx and NOx emissions limits in coastal Emission Control Areas (ECAs) and the IMO’s global sulphur cap. Furthermore, its unparalleled emissions performance effectively insulates shipping companies from the impact of future, more demanding, local emissions regulations.
*Photo credit : John Calambokidis/Cascadia Research Collective
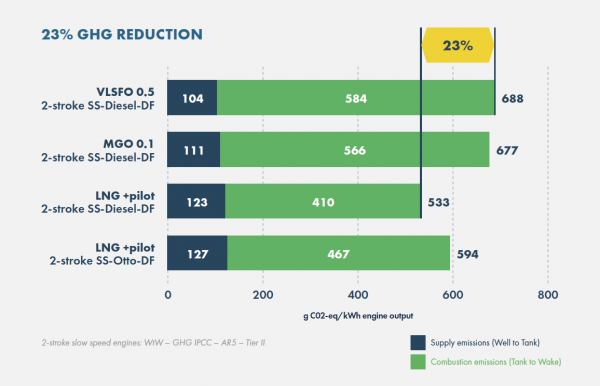
Uniquely, among alternative marine fuels, LNG is able to offer immediate GHG reductions, of up to 23% on a well-to-wake basis in its fossil form including the impact of methane emissions, when compared to conventional marine fuels. Consequently, it is compliant until 2039 with FuelEU Maritime and offers the lowest cost of compliance with EU ETS, and the IMO’s proposed Net Zero Framework.
In the long term, the use of liquefied biomethane (LBM or bio-LNG) and e-methane provides LNG dual fuel vessel owners and operators a pathway to net zero GHG emissions, ensuring these assets are never stranded by regulations.
There are no waste disposal or discharge issues associated with the use of LNG in contrast to exhaust gas treatment systems, or scrubbers used by shipping companies, which continue to burn high sulphur, heavy fuel oil. Finally, LNG poses no pollution risk to ocean environments through fuel spills in contrast to traditional marine fuels.

INDEPENDENT STUDY CONFIRMS LNG REDUCES SHIPPING GHG EMISSIONS BY UP TO 23%
13th April 2021
Peer-reviewed well-to-wake study updates definitive figures for GHG emissions from LNG as a marine fuel