Decarbonisation
LNG offers a decarbonisation pathway for the global shipping industry now.
In combination with efficiency measures being developed for new ships in response to the IMO’s Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI), LNG, in its fossil form, provides a way to meet the IMO’s carbon intensity reduction target of 40% by 2030 for international shipping.
Offering up to a 23% reduction in GHG emissions, LNG-fuelled ships are compliant with FuelEU Maritime, the EU’s precedent-setting shipping decarbonisation regulation, until 2039.
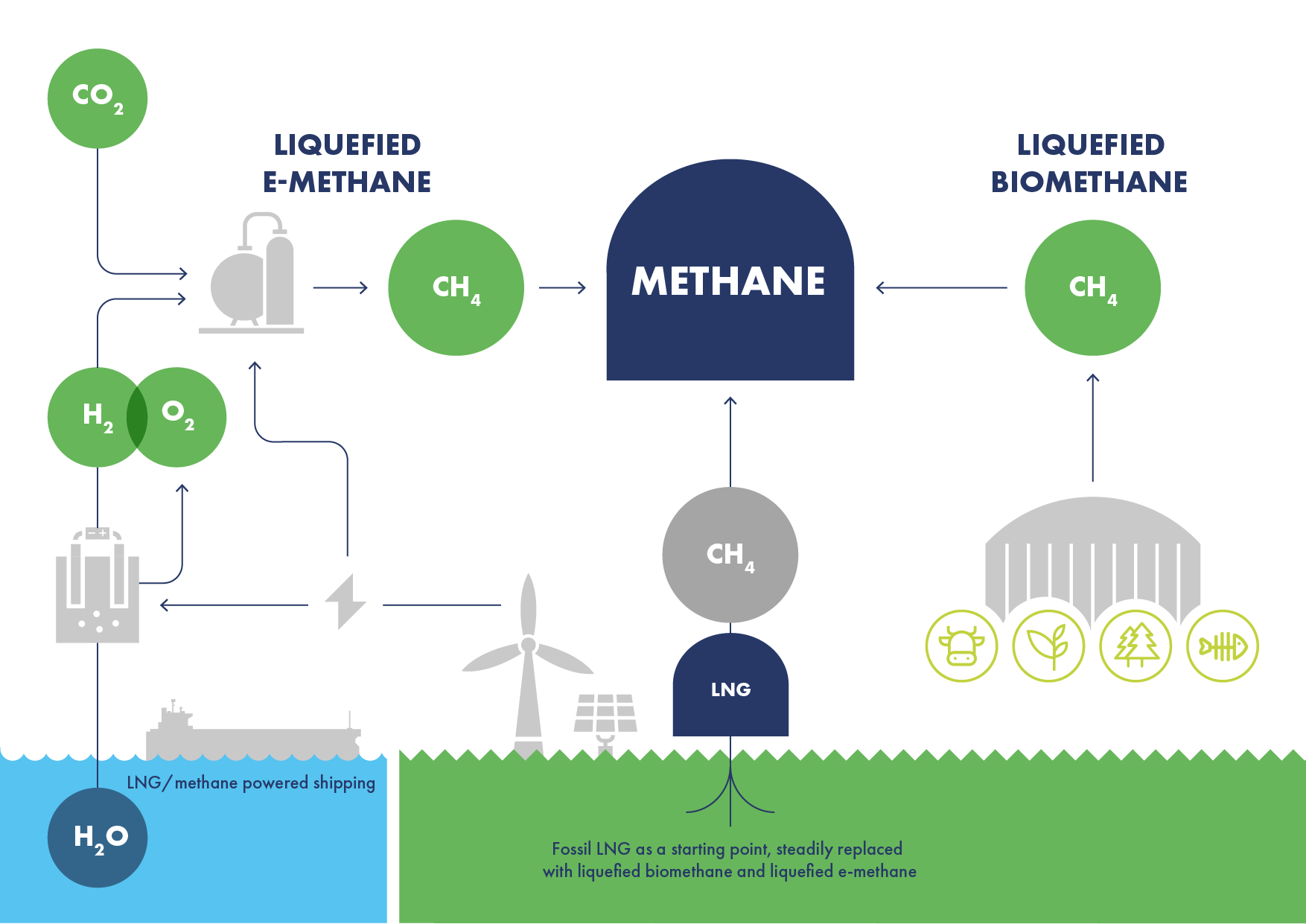
Longer-term LNG offers a decarbonisation pathway for shipping to become carbon-neutral through the use of liquefied biomethane (LBM, also known as bio-LNG, or RNG) produced from biomass and liquefied e-methane (also known as e-LNG) produced from renewable electricity.
Liquefied biomethane and e-methane are scalable solutions for the maritime sector, with estimated sustainable global supplies potentially exceeding the demands of shipping in the future, and likely to be commercially competitive relative to other low- and zero-carbon fuels. Further, the growing LNG-fuelled fleet could use liquefied biomethane or e-methane without requiring major modifications, and the existing supply infrastructure will remain fit for bunkering purposes with either fuel.
New independent study confirms bio-LNG’s role in shipping’s decarbonisation
5th October 2022

